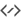Coordonnées géographiques¶
Jason Harris
Locations on Earth can be specified using a spherical coordinate system. The geographic (“earth-mapping”) coordinate system is aligned with the spin axis of the Earth. It defines two angles measured from the center of the Earth. One angle, called the Latitude, measures the angle between any point and the Equator. The other angle, called the Longitude, measures the angle along the Equator from an arbitrary point on the Earth (Greenwich, England is the accepted zero-longitude point in most modern societies).
En combinant ces deux angles, on peut spécifier tout endroit sur Terre. Par exemple, Baltimore dans le Maryland (USA) possède une latitude de 39,3 degrés nord et une longitude de 76,6 degrés ouest. En d'autres mots, si l'on dessine une ligne entre le centre de la Terre et un point qui se trouve à 39,3 degrés au-dessus de l'équateur et à 76,6 degrés à l'ouest de Greenwich, alors elle passera à travers Baltimore.
The Equator is obviously an important part of this coordinate system; it represents the zeropoint of the latitude angle, and the halfway point between the poles. The Equator is the Fundamental Plane of the geographic coordinate system. All Spherical Coordinate Systems define such a Fundamental Plane.
Lines of constant Latitude are called Parallels. They trace circles on the surface of the Earth, but the only parallel that is a Great Circle is the Equator (Latitude=0 degrees). Lines of constant Longitude are called Meridians. The Meridian passing through Greenwich is the Prime Meridian (longitude=0 degrees). Unlike Parallels, all Meridians are great circles, and Meridians are not parallel: they intersect at the north and south poles.
Astuce
Exercice
Quelle est la longitude du pôle Nord ? Sa latitude est de 90 degrés nord.
C'est une question piège. Le longitude n'a aucune signification au Pôle Nord (ou au Pôle Sud). Il possède toutes les longitudes à la fois.